IoC, Dependency Injection and Dependency Inversion
Understand Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection and Dependency Inversion. How apply it together ?
Resources
Introduction
In this article we come back about one of the most important principles to create a flexible, light coupled and well maintenable application.
IoC : Inversion of Control
DI : Dependency Injection
DIP : Dependency Inversion Principle
Definition
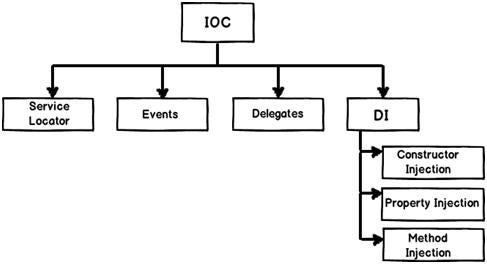
IoC
Inversion of Control (IoC) is a design that helps manage and invert the flow of objects in a software application.
Traditionnaly when a class ReservationService has dependency to another class ReservationDAO, ReservationService controls the instantiation of its dependencies.
class ReservationService {
private ReservationDAO reservationDAO;
private void bookCar(Car car, Date date) { … }
}A simple answer would be to say that each object in the ReservationService class is responsible for creating the ReservationDAO object. In object-oriented programming, this type of behaviour is very easy to implement with a constructor.
class ReservationService {
private ReservationDAO reservationDAO;
public ReservationService() {
this.reservationDAO = new ReservationDAO();
}
private void bookCar(Car car, Date date) { … }
}It’s the tradionnal flow of the objectif creation.
What’s wrong ?
This solution, although simple, is problematic. By doing this, we introduce a strong coupling between the ReservationService class and the reservationDAO class :
If
reservationDAOis refactored we must rebuild, retest and redeployreservationDAOandReservationService.
IoC the solution !
In IoC, this control is inverted, and a container takes on the responsibility of managing the dependencies, allowing for greater modularity, flexibility, and testability.
ReservationServiceis no longer responsible for instantiatingReservationDAOobject.
So, who’s responsible ? See the next section Dependency Inversion
Dependency Injection (DI)
Inversion of Control can be carried out in different ways. The most common method is Dependency injection.
Dependency Injection helps us to achieve “who’s responsible to create ReservationDao object” ? DI is about how one object acquires a dependency
class ReservationService {
private ReservationDAO reservationDAO;
public ReservationService(ReservationDAO pReservationDAO) {
this.reservationDAO = pReservationDAO;
}
private void bookCar(Car car, Date date) { … }
}With DI we pass the
ReservationDAOobject as a parameter in the constructor. TheReservationServiceobject acquires the dependencyReservationDAOby Constructor Injection
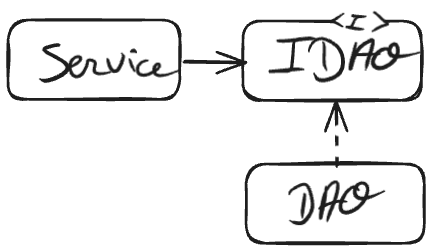
Dependency Inversion (DIP)
Introduced by Rober C. Martin in the series of SOLID Principle the Dependency Inversion Principle is a specific methodology for loosely coupled software modules.
High-level modules should not import anything from low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions (e.g., interfaces).
Abstractions should not depend on details. Details (concrete implementations) should depend on abstractions.
In our example, we translate the following rules by adding an interface between the Service ans the DAO
class ReservationDAO implements IReservationDAO {
}
class ReservationService {
private IReservationDAO reservationDAO;
public ReservationService() {
this.reservationDAO = new RepositoryDAO(); // No injection
}
private void bookCar(Car car, Date date) { … }
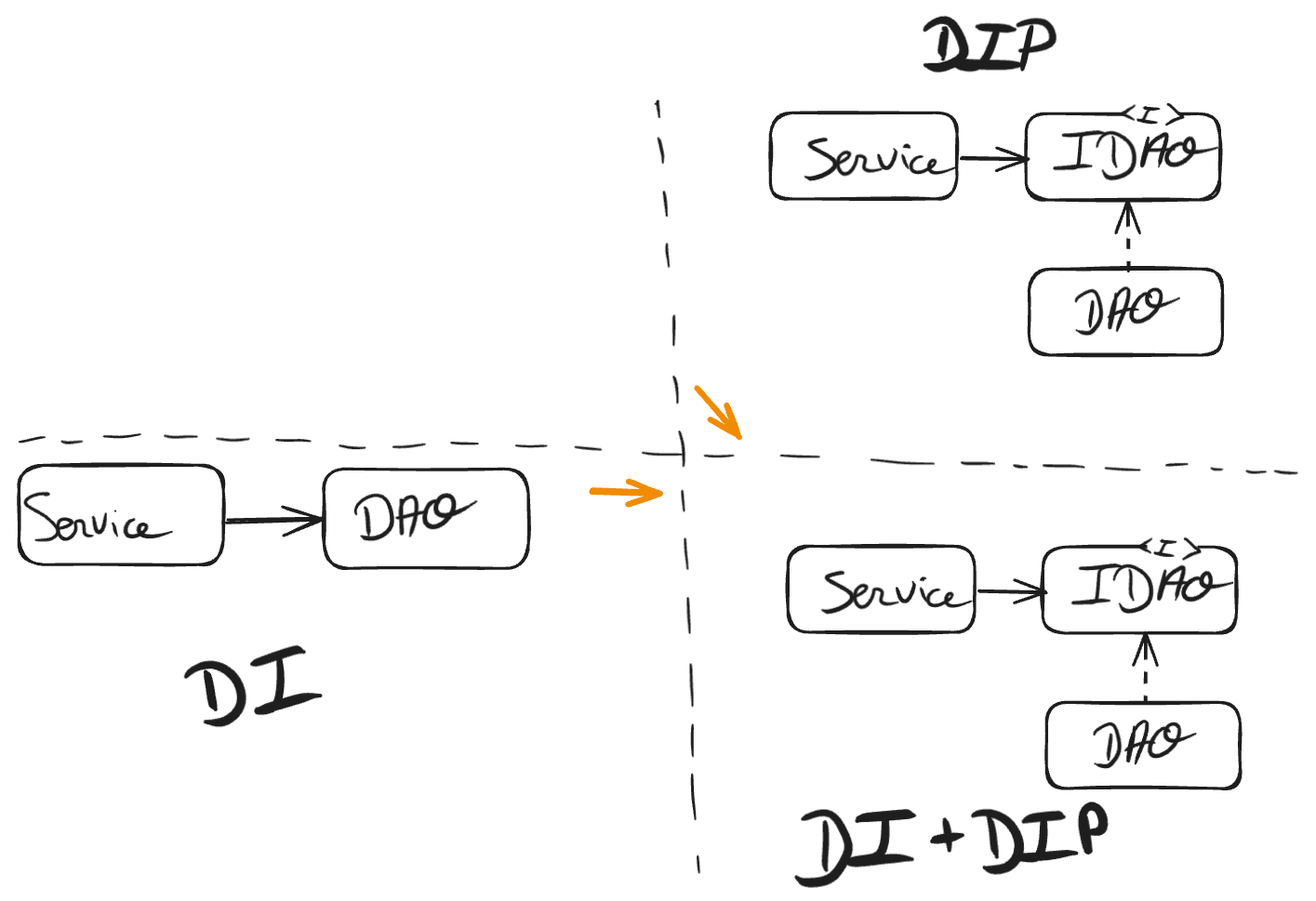
}Apply it together
DI + DIP
class ReservationService {
private IReservationDAO reservationDAO; // Interface
public ReservationService(IReservationDAO pReservationDAO) {
this.reservationDAO = pReservationDAO; // injection
}
private void bookCar(Car car, Date date) { … }
}DIP : The class
ReservationServicemust not be modified due to a change inReservationDAOFor example, if the algorithm is updated in the
update()method,ReservationServiceis now decoupled and does not need to be rebuilt, retested and redeployed
DI :
ReservationDAOobject is created outside of the class that uses it.The code is now better readable, testable and maintenable because we can easily change the implementation without rebuild and redeploy the class
ReservationService
main() {
IReservationDAO reservationDAO = new ReservationDAO();
ReservationService reservationService =
new ReservationService(reservationDAO);
}Now if we have a new algorithm, we only have to change the main() method to update the software
main() {
// IReservationDAO reservationDAO = new ReservationDAO();
IReservationDAO reservationDAO = new NewReservationDAO();
ReservationService reservationService =
new ReservationService(reservationDAO);
}Conclusion
Dependency Injection is a subtype of IoC
IoC and Dependency Inversion are used together to create low coupled software.